Pain Relief & accelerated Healing with CBD & CBG
- The Health Master

- Mar 1, 2024
- 4 min read
Updated: Apr 28, 2024
Is CBD & CBG good for pain relief and accelerated healing? A new study has come out from Penn State scientists. Pain can make life intolerable. People urgently need help to relieve all kinds of pain, whether from a debilitating injury, a chronic condition, or general aches and discomfort.
We hear from thousands of people in our community about how CBD products take their pain away. Science is increasingly explaining these seemingly miraculous benefits. A new study conducted at Penn State looked at the effectiveness of treating bone injuries with CBD and CBG. Together, these two cannabinoids were found to not only be similarly effective in providing pain relief as conventional NSAID medications (such as Aspirin)–but they actually helped generate higher volume and mineral density in bones healing from fractures.
Here's the conclusion of the research: CBD and CBG can relieve pain and speed the healing of bones. There’s a lot to learn when it comes to CBD and all the ways that hemp can help you feel your best. If you’re struggling with discomfort of any kind, just reply to this email. Our in-house experts will be in touch to guide you on a personalized journey towards tailoring the perfect routine for you.
2 cannabis compounds may boost pain relief, speed up healing of fractured bones
Two compounds found in cannabis may offer hope to bone fracture patients for pain management and even accelerated healing. Researchers from Penn State University believe their promising findings could revolutionize how we approach bone fracture treatment using cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG).
There are more than 178 million people worldwide suffer from bone fracture injuries every year. The current methods of pain management, typically relying on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin, have their limitations.
According to Reyad Elbarbary, associate professor of orthopedics and rehabilitation at Penn State College of Medicine and the study’s corresponding author, NSAIDs, while effective in pain management, hinder the crucial first step in fracture healing – inflammation.
“NSAIDS may help patients manage pain, but they also reduce inflammation, which is a crucial first step in fracture healing,” says Elbarbary in a university release. “An alternative for pain management is needed that does not prevent inflammation from occurring.”
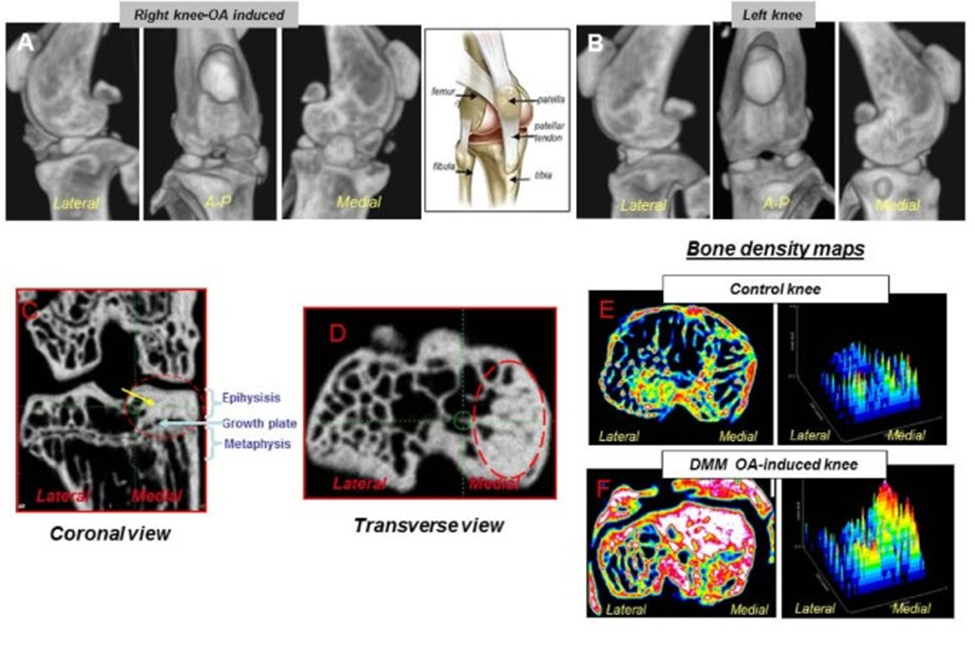
Penn State scientists initially set out to measure the individual pain-alleviating properties of CBD and CBG. This study is the first to examine the effects of cannabinoids, specifically in the context of fracture healing and pain management. Cannabinoids demonstrated effectiveness comparable to NSAIDs in pain management, but researchers were also astonished to discover their positive impact on the fracture healing process.
Using advanced techniques such as immunofluorescence microscopy & microcomputer tomography imaging, researchers examined various aspects of the fracture healing process, including bone density, bone strength, and the expression of essential genes involved in fracture healing.
In the early treatment phase, CBD and CBG were associated with an increased presence of periosteal bone progenitors, which ultimately transform into specialized bone cells vital for bone tissue formation. During the later stages of healing, CBD and CBG accelerated the body’s absorption of minerals, reinforcing newly formed bone.
“Both treatments led to higher bone volume fraction and mineral density than with NSAID treatments, which leads to a functional and healthy newly formed bone,” notes Elbarbary. “We still have a lot to learn about the biological mechanisms behind what we observed.”
The future research agenda will focus on defining the cellular and molecular processes responsible for the cannabinoids’ roles in both the early and late stages of fracture healing. Additionally, efforts will be directed towards developing a clinical formulation suitable for adult fracture patients. While CBD has already received approval from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating Epilepsy and seizures in children, finding an appropriate formulation or dosage for adults dealing with bone fractures will be a crucial next step.
The study is published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.
CBD and CBG is NOT the same as smoking marijuana
Cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG) are two of the most well-known cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. Both CBD and CBG offer a variety of potential health benefits, but they are different from smoking marijuana in a number of ways.
CBD and CBG are non-psychoactive. This means that they do not produce the “high” associated with smoking marijuana. THC, the main psychoactive compound in marijuana, binds to cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptors in the brain. CBD and CBG, on the other hand, do not bind to CB1 receptors to the same extent, which is why they do not produce a psychoactive effect.
CBD and CBG are less likely to cause side-effects. Smoking marijuana can cause a number of side-effects, including dry mouth, red eyes, anxiety, and paranoia. CBD and CBG are much less likely to cause the side-effects. In fact, both CBD and CBG have been shown to be safe and well-tolerated in humans.
CBD and CBG products are available in a variety of forms, including oils, capsules, edibles, and topicals. This makes it easy to find a form of CBD or CBG that is right for you. Smoked marijuana, on the other hand, is only available in one form.
CBD and CBG products are legal in most jurisdictions, including in the United States. Smoked marijuana, on the other hand, is still illegal in many places.
DISCLAIMER
All products are Federal Farm Bill Compliant and contain less than 0.3% THC. FDA DISCLOSURE: The statements regarding these products have not been evaluated by the FDA. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease, consult your health physician before use. The Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act requires placement of this notice.











I like the article you wrote very much, which has benefited me a lot. I have been very in interested in CBD & CBG for pain recently. There is a very good store. This is it's website: TheVapeSocietyCBD.com If you are interested, you can come in and browse and choose the products that are best for you.